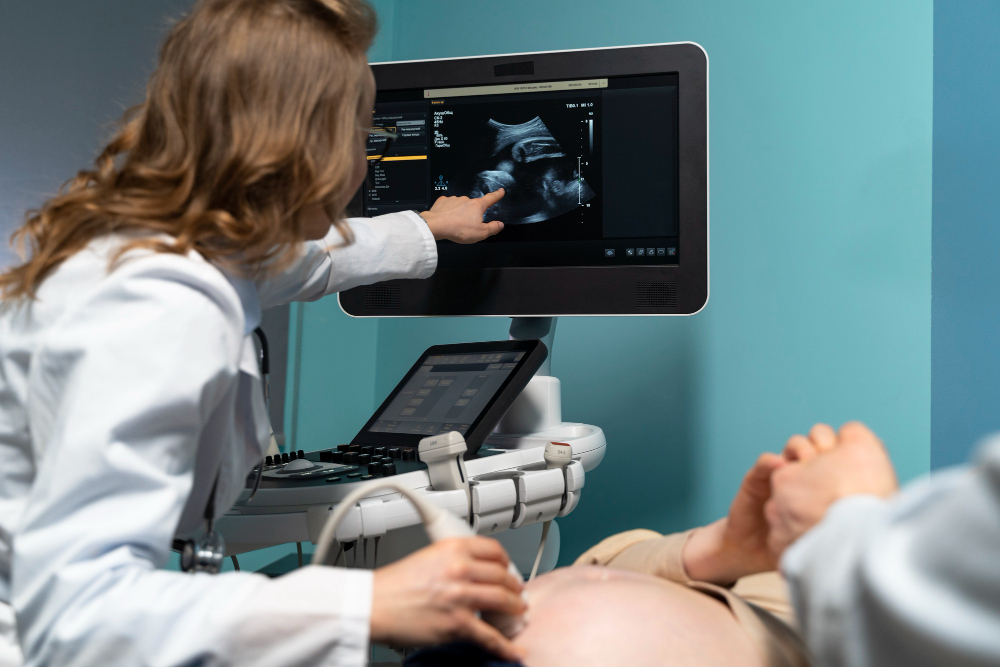
Ultrasound, also known as sonography, is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It is widely used in diagnostic medicine due to its safety, effectiveness, and ability to capture real-time images of organs and tissues without the need for radiation.
Ultrasound works by emitting sound waves through a transducer, which is placed on the skin over the area being examined. These sound waves travel through the body and bounce off tissues, organs, and fluids. The reflected sound waves are then captured by the transducer and converted into images displayed on a monitor. The technique allows for detailed visualization of the body’s internal structures in real time.
Ultrasound is used for a variety of diagnostic purposes, including:
Ultrasound is highly effective in providing clear images with real-time feedback. It is a safe procedure with no known risks, making it ideal for use in pregnant women and for monitoring children. Additionally, ultrasound is painless, quick, and non-invasive, making it accessible for a wide range of diagnostic purposes.
Ultrasound is considered safe because it does not use ionizing radiation, unlike X-rays or CT scans. It is one of the most commonly used imaging techniques in healthcare, offering valuable insights without harm to the patient.